Specific Gravity Test on Cement | Determine the specific gravity of cement - lceted
Objective
To determine the specific gravity of cement.
Theory and Scope
Specific gravity is normally
defined as the ratio between the mass of a given volume of material and the mass of an equal volume of water. One of the
methods of determining the specific gravity of cement is by the use of a liquid such as water-free kerosene which
does not react with cement. A specific gravity bottle or a standard Le Chatelier specific gravity
flask may be used.
In addition to hydraulic
cement, the Le Chatelier specific gravity flask can also be used to obtain the specific gravity of dust, sand, and other fine
materials.
Also read: Laboratory Tests On Cement | 8 Different Types Of Cement Test
Apparatus
Weighing balance; Le Chatelier specific gravity flask with
a ground glass stopper, Specific gravity bottle; Kerosene free from water; Constant temperature
water bath.
Description of Apparatus
The Le Chatelier flask shown
in Fig. below is made of thin glass having a bulb at the bottom. The capacity of the bulb is nearly 250 ml. The bulb is 78 mm
in mean diameter. The stem is graduated in millilitres; a small oval bulb in the neck holds 17 ml, below this bulb
are graduations from 0−1ml; above the bulb, the neck is graduated from 18−24 ml. The portion above the 24
ml mark is in the form of a funnel having a top diameter of 50 mm. Thus the total capacity of the stem of the bulb is 24 ml. A glass stopper or nipple is fitted in the stem to cover the flask.
Procedure
Step
1:
With a specific gravity bottle
(a) Weigh the specific gravity bottle dry. Let the mass
of the empty bottle be W1.
(b) Fill the bottle with distilled water and weigh. Let
the mass be W2.
(c) Wipe dry the specific gravity bottle and fill it
with kerosene and weigh. Let this mass be W3.
(d) Pour some of the kerosene out and introduce a
weighed quantity of cement, W5 (about 50 g) into the bottle. Roll the bottle gently in an inclined
position until no further air bubbles rise to the surface. Fill the bottle to the top with kerosene and weigh it.
Let this mass be W4.
(e) From these data calculate the specific gravity of
the cement, S.
The specific gravity of kerosene,
Volume of bottle =
W2 – W1
Volume of cement = W5/S
Volume of kerosene after the cement has been added = (W2 – W1) − W5/S
Where from a mass of kerosene after cement has been added =
[(W2 – W1) − W5/S] s
Therefore, [(W2
– W1) − W5/S ] s + W5 + W1 = W4
Substituting the value of s and simplification,
Therefore, specific gravity of cement,
Observations and Calculations
Step
2:
With Le Chatelier flask
Apparatus
for determining the specific gravity of cement
1. Dry the flask carefully and fill with kerosene or
Naphtha to a point on the stem between zero and
1 ml.
2. Dry the inside of the flask above the level of the
liquid.
3. Immerse the flask in a constant temperature water
bath maintained at room temperature, for a sufficient period before taking any reading so as to
avoid variation greater than 0.2°C in the temperature of the liquid in the flask.
4. Record the level of the liquid in the flask as the initial reading, V1.
5. Place a weighed quantity of cement, W1
(about 60 g) into the flask so that level of kerosene rises to about say 22 ml mark. Care is taken to avoid
splashing and to see that cement does not adhere to the sides of the flask above the liquid.
6. After putting all the cement into the flask, insert the
nipple and roll the flask gently in an inclined position to free the cement from the air until no further
air bubble rises to the surface of the liquid.
7. Keep the flask back in a constant temperature water
bath and note down the new liquid level as the final reading, V2.
8. Calculate the specific gravity, S.
Observations and Calculations
Precautions
1. The kerosene or Naphtha
used should be free from water.
2. The specific gravity
bottle and the Le Chatelier flask should be held in a constant temperature
water bath sufficiently long to ensure the same temperature before each weighing is made.
3. Duplicate determination
of specific gravity should agree within 0.01.
4. While introducing
cement, care should be taken to avoid splashing and cement should not adhere to
the inside of the flask above the
liquid.
Also read: What Is Specific Gravity? How To Determine Water Content Using It
Discussion
In case specific gravity
bottle shown in Fig. above is used, it is necessary to determine the specific
gravity of kerosene or other liquid used
and all the measurements are made entirely by mass. If Le Chatelier flask
is used, some of the measurements are
made by volume and it is not necessary to know the specific gravity of kerosene. The relative density of kerosene is
0.8. The specific gravity of ordinary Portland cements is in the range of 2.15.




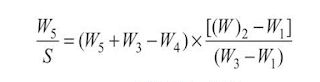
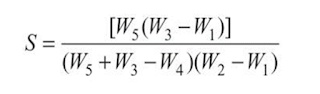










No comments:
Post a Comment