UNDERPINNING
Underpinning is the method
of supporting structures while providing new foundations or strengthening the
foundation or carrying out repairs and alterations without affecting the
stability of the existing structures.
Dead-shores
used for repairs
USES OF UNDERPINNING
Underpinning techniques are
adopted under the following situations:
(i) To strengthen the existing shallow foundation of a building when an adjoining building has to be
constructed with a deep foundation.
(ii) To safeguard the
existing structure from the danger of excessive or differential settlement.
(iii) To deepen and widen
an existing foundation to increase the bearing capacity of the foundation soil.
(iv) To build a basement
floor to an existing building.
(v) To lift a building
fully or partly to alter the foundation so as to prevent waterlogging.
PRECAUTIONARY
MEASURES BEFORE UNDERPINNING
The
following general measures should be undertaken before starting the
underpinning operations:
(i) The existing strength
of the building should be ascertained before resorting to underpinning (e.g.,
inferior material used or use of construction method which is not standard or
poor workmanship).
(ii) Temporary support
should be provided by adequate shoring and strutting wherever needed.
(iii) During underpinning
of buildings, a watch on possible movements should be checked and rectified
then and there.
(iv) No damage should be
caused to the adjoining structures.
(v) It should be ensured
that no obstruction is created to the passage of people or vehicles in the
adjoining areas.
METHODS OF
UNDERPINNING
Several methods are
available for underpinning foundations but four routine methods which are used
in general, are:
1. Pit Method
2. Pile Method
3. Pier Method
4. Chemical Method
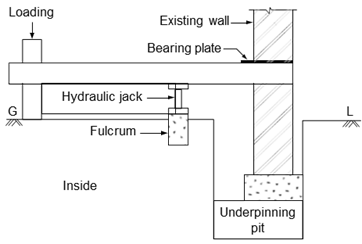
1. Pit Method
Generally underpinning by
pit method is carried out by excavating slowly in stages. For this, the existing
wall is divided into suitable widths of about 1.20–1.50 m. Holes are made in the
existing wall in the required points. Needles with bearing plates are then
inserted through these holes and supported on jacks, Fig. below. This is
followed by excavation, first up to the existing foundation level and then to
the required depth.
Pit
method
During
the process of excavation, the following precautions are to be taken to avoid
formation of crakes or settlement:
(i) Excavation should be done one at a time preferably
starting at the middle and progressing sideways.
(ii) Proper timbering is to be provided to the excavated
trenches.
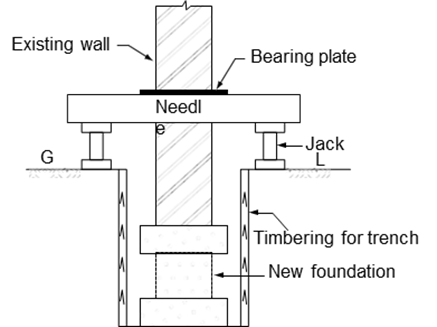
(iii) Instead of a central needle beam, a cantilever needle the beam may be adopted as shown in Fig. below.
(iv) After completion of the excavation, foundation concrete
is laid.
(v) A suitable connection between the old foundation and a new foundation has to be made using vertical mild steel bars.
(vi) After the new foundation is completely set, then
only the needle beams and raking shores are removed.
Support
by cantilever needle
2. Pile Method
The pit method may be impracticable or uneconomical in the
following cases:
(i) Waterlogged area
(ii) Heavy loads on existing structures
(iii) Loads to be transferred to a deeper depth
In such situations, the pile method may be adopted.
In this method, the piles
are driven along both sides of the existing wall. Then needles in the form
of pile caps are provided through the existing wall as shown in Fig. below.
Thus, the existing wall is relieved of the loads coming on it.
Underpinning
by piles
This method is particularly
useful in clayey soils and for waterlogged areas and for walls bearing heavy
loads. In the case of light structures piles are driven along with the structure and
then brackets or cantilever needles are provided.
In another approach,
pre-cast piles are installed beneath the existing foundation using jacks and
digging approach pits. The materials surrounding the pit is removed by water
jets or airlifts and then filled with cement concrete.
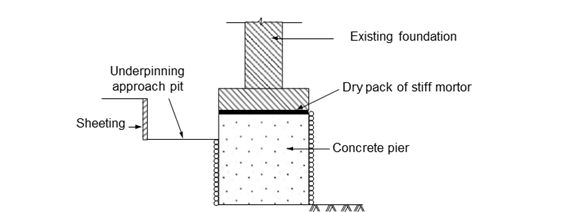
3. Pier Method
This method is generally
resorted to in the dry ground. This is a simple method of underpinning. It
involves the installation of piers under foundations of structures through the
approach pits. Filling the pits with concrete and finally wedging up to
transfer the loads to the new piers, Fig. below.
Underpinning
by pier
4. Chemical Method
In this method the
foundation soil is consolidated by employing chemicals.
Perforated pipes are a driver
in an inclined direction beneath the foundation, Fig. below. The slopes are
provided such that the entire area under the existing footing corners under the
area used to be strengthened.
Chemical
method
After the pipes are
installed, a solution of sodium silicate in water is injected through the pipes.
This is a two-injection method. The pipes are withdrawn and at the time of
withdrawal of pipes, calcium or magnesium chloride is injected through the
pipes. A chemical reaction takes place between these two chemicals and the soil
is strengthened by consolidation. This method is suitable for granular soils.
SOURCE: BUILDING CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS AND TECHNIQUES | P. PURUSHOTHAMA RAJ
If you find
This information is helpful, please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article...











No comments:
Post a Comment