\
SELECTION AND DESIGN OF SIMPLE FOUNDATIONS
Foundations Selection Procedure
The selection of a foundation suitable for the type of
structure to be constructed or for a given size depends on several factors.
Following are the general steps to be followed in choosing the type of
foundation.
(i) Necessary data about the type of structure and the
loads anticipated to be carried by the structure are collected.
(ii) Adequate information about the sub-soil condition
through a suitable soil investigation is got.
ALSO
READ: HOW
TO CHOOSE THE CORRECT FOUNDATION FOR YOUR CONSTRUCTION?
(iii) The possibility of constructing a different
foundation keeping in mind the basic design criteria for a foundation is
explored. During this exercise, all unsuitable types may be eliminated in the
preliminary choice.
(iv) One or two types of foundations based on the
preliminary studies which may be a shallow or deep foundation, are selected and
more detailed studies regarding the stability of the foundation and
super-structure is carried out.
(v) Cost estimates of one or more chosen foundations are
worked out.
(vi) Three types of foundations to satisfy all the
requirements are finally decided.
Foundations
Design Procedure
The following general steps have to be adopted in the
design of foundations:
1. A soil investigation has to be carried out as discussed in earlier posts.
2. It is necessary to compute the total load (both dead and
live load) and the distribution has to be assessed.
3. It is to assess the total and differential settlement
which the structure may undergo.
4. Based on the type of soil and the structure and load
the type of foundation is decided as discussed in earlier posts.
5. The appropriate allowable soil pressure has to be
determined for the selected type of foundation.
6. The type of material for the foundation has to be
decided.
7. Alternate designs are to be made before finalization.
8. Cost estimate has to be made and any further
modification may be made keeping in view the economy and life of the structure.
Design Procedure of Shallow Foundations
Following guidelines may be taken while designing
shallow foundation other than rafts and mats.
(i) In the case of wall footing the width of the foundation
should be computed based on the allowable soil pressure.
(ii) In case no footings are to be provided to the walls
the width of the foundation should be equal to three times the width of the wall.
(iii) In the case of piers the width of the foundation is equal
to the square roots of the total load of the pier divided by the allowable soil
pressure.
(iv) For unreinforced strip footings the thickness
should not be less than the projection from the base of the wall. It should not
be less than 150 mm where the foundations are laid at more than one level.
(v) For unreinforced column footing the spread of
footing maybe 1 vertical to one horizontal.
(vi) As a general rule, the shallow foundation should be
taken down to a depth where the allowable bearing capacity is adequate.
(a) As for as possible the foundation should be kept
above the groundwater table.
(b) In order to safeguard against minor soil erosion,
a minimum depth of 500 mm is provided for strip or column foundation
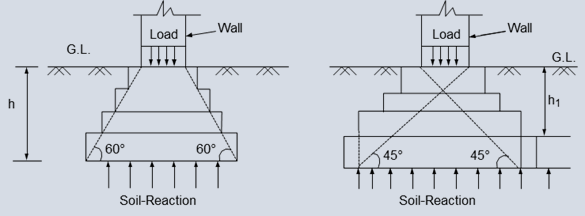
(c) The depth of foundation can be also determined by
plotting the pressure distribution lines (below figure).
h1, h2 = Depth of
footing, Depth of base concrete
h = Depth of foundation
Then, h = h1 + h2
(d) Minimum depth of
foundation for loose soils may be obtained from Rankine’s formula, i.e.,
Also
read: HOW
TO CALCULATE DIMENSIONS OF FOUNDATION
Where,
h = Minimum depth of foundation in m
w = Weight of soil in kg/m3
f = Angle of repose
p = Load in soil kg/m2
Where,
a = offset of concrete in cm
f = safe modulus of rupture in kg/m2
Design Procedure of Piles
Following guidelines may be considered in the design of
piles
(i) Direct vertical load coming on the pile should be
considered.
(ii) In the case of driven piles, the impact stresses
induced due to pile driven is taken into account.
(iii) Bending stresses induced due to bending in piles
and due to eccentricity to be accounted.
(iv) Lateral forces due to wind, waves, water, current,
ice sheets, the impact of ships are to be accounted
(v) Forces due to uplift may also be considered.
(vi) If the area is earthquake-prone area necessary
modifications have to be made.
(vii) Load carrying capacity of the pile is computed based
on the type of pile. Pile load tests can be done for all types of piles. For
driven piles, pile driving formulas can be used.
One such formula is ENR formula which is derived on the basis of work-energy
theory. The ENR formula has been modified by Hiley as the ultimate pile load,
Qu is given as
Where,
ç = Hammer efficiency
W = Weight of hammer
h = Height of fall
S = Final set
çb = Efficiency of the blow.
C = Sum of the temporary elastic compression of the
pile.
If you find
This information is helpful, please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article.



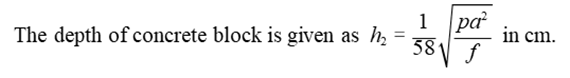







No comments:
Post a Comment