COMPONENT PARTS OF A BUILDING
The basic requirements a building should satisfy in
design and performance are:
· It
must be strong enough to withstand the loads coming on it including the
self-weight, live load, wind load and earthquake load.
· It
must not deflect under the loads.
· It
must give comfort and convenience to the inhabitants.
BUILDING COMPONENTS AND THEIR BASIC
REQUIREMENTS
A
building broadly consists of three parts:
1. Foundation
2. Plinth
3. Superstructure
Foundation
The foundation is the most
critical part of any structure and most of the failures are probably due to
faulty foundations. Hence, it is highly essential to secure a good foundation to
maintain the stability of the structure. A good foundation must remain in
position without sliding, bending, overturning or failing in any other manner.
The foundation of any structure should be laid much
below the surface of the ground in order to attain the following:
a. To
secure a good natural bed.
b. To
protect the foundation courses from atmospheric influences.
c. To
increase the stability of the structure against overturning due to wind uplift.
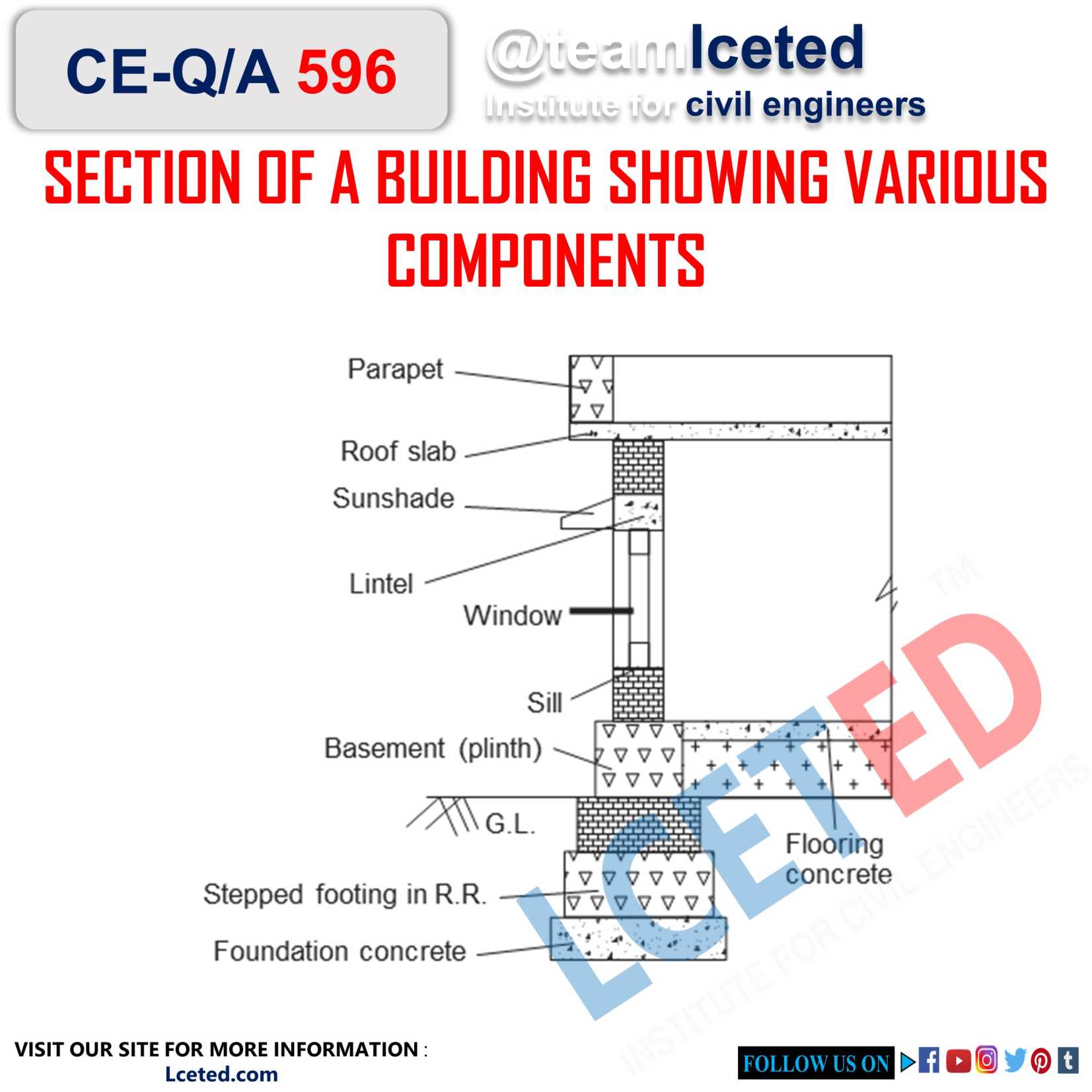
Section
of a building showing various components
The primary function of the
foundation is to transmit the anticipated loads safely to the soil below. The
foundation in a building structure is supposed to satisfy the following basic
requirements in its design and construction:
a. To
distribute the total load coming on the structure over a large bearing area so
as to prevent it from any movement.
b. To
load the bearing surface or area at a uniform rate so as to prevent it from any
movement.
c. To
prevent the lateral escape or movement of the supporting material or
alternatively to ensure the stability of the structure against sliding.
d. To
secure a level or firm natural bed upon which to lay the course of masonry and
also support the structure.
e. To
increase the stability of the structure as a whole to prevent it from
overturning or sliding against disturbing forces such as wind, rain and
frost.
Plinth
This is the portion of the
structure between the surface of the surrounding ground and the surface of the
floor immediately above the ground. The thickness of the plinth wall depends upon
the weight of the superstructure and the width of the foundation concrete. The
minimum height of the plinth is usually kept as not less than 4.5 cm.
The
plinth wall should satisfy the following requirements in a building structure
in its design and construction:
a. To
transmit the load of the superstructure to the foundation.
b. To
act as a retaining wall so as to keep the filling in position below the raised
floor or the building.
c. To
protect the building from dampness or moisture.
d. To
enhance the architectural appearance of the building.
Walls and piers in the superstructure
The primary function of the wall is to enclose or divide
space. Piers are usually in the form of a thickened section of a wall, placed
at intervals along the wall to take concentrated vertical loads or to provide
lateral support to the wall. These walls may be built of different materials
such as brick or stone masonry, plain concrete and reinforced masonry.
A load-bearing wall should satisfy the following requirements:
a. Strength: A the wall should be strong enough to take up the loads safely. The loads coming in
the wall includes its own weight, weight by superimposed loads and bilateral
pressures like the wind.
b. Stability: It
should be stable against overturning by lateral forces and buckling caused by
excessive slenderness.
c. Weather
Resistance: All the external walls whether load-bearing
or panel constructions should provide adequate resistance to rain, sun and
wind.
d. Fire
Resistance: The walls should offer sufficient resistance
to fire as they behave as vertical barriers for spread of fire in the horizontal
direction.
e. Heat
Insulation: It should be possible for walls to attain
insulation against heat.
f. Sound
Insulation: The walls should be made of such materials
and by such technique so as to insulate the building against sound.
g. Privacy
and Security: The walls should provide sufficient privacy
and afford security against theft.
Floors
The main function of a floor
is to provide support for occupants, furniture and equipment of a building, and
the function of providing different floors is to divide the building into
different levels for creating more accommodation within the limited space (Table).
A
floor should satisfy the following requirements:
a. Strength
and Stability: All the floors, whether basement, ground or
upper should be strong enough to support the floor covering and other
superimposed loads.
b. Durability
and Damp Prevention: The floors provide a clean, smooth,
impervious, durable and wear-resisting surface.
c. Heat
Insulation: Insulation against heat should be provided
in case of ground and basement floors, especially when suspended and ventilated
timber floors are used.
Criteria
for Calculating Floor Areas and Height of Structures
|
TYPE OF BUILDING |
CUBIC CONTENTS PER
CAPITA (M3) |
FLOOR AREA PER
CAPITA (M3) |
|
Residential buildings |
9 |
2.5–9 |
|
Dormitories |
12–15 |
3-4 |
|
Educational buildings |
4.5–7.5 |
1-2 |
|
Institutional buildings |
30 |
8–10 |
|
Industrial buildings |
7.5 |
2–2.5 |
d. Sound
Insulation and Fire Resistance: The insulation against
sound and fire should be provided in the case of upper floors as they act as
horizontal barriers for the passage of sound and fire in a vertical direction.
Doors and windows
The main function of doors
in a building is to serve as a connecting link between internal parts and to
allow free movement to the outside of the building. Windows are generally
provided for proper ventilation and lighting and their number should be
determined according to the requirements.
Doors
and windows should satisfy the following requirements:
a. Weather
Resistance: They should be strong enough to resist the
adverse effects of weather.
b. Sound
and Thermal Insulation: They should be capable of being made
airtight to achieve insulation against sound and heat.
c. Damp
Prevention and Termite Prevention: They should not be affected
by white ants and the moisture penetration as this will reduce the strength and
durability.
d. Fire
Resistance and Durability: They should offer fire resistance and
should be durable.
e. Privacy
and Security: They should offer sufficient privacy without
inconvenience or trouble and security against theft.
Sills, lintels and weather shades
Window sills are provided
between the bottom of the window frame and the wall below to protect the top of
the wall from wear and tear. The openings are provided in the wall of a
building to accommodate the doors and windows. The actual frame of a door or
window is not strong enough to support the weight of the wall above the opening
and a separate structural element is, therefore, introduced between the top of
the window frame and the wall coming over it. This is known as the lintel.
Weather shades are generally combined with lintels of windows to protect them
from weathering agencies.
Roofs
A roof is the uppermost
part of a building whose main function is to enclose the space and to protect
the same from the effects of weather elements. A good roof is just as essential
as a safe foundation. As a well-designed foundation secures the building
against destruction starting at the bottom, similarly a good roof affords
protection for the building itself and what the building contains and prevents
destruction from the top.
A
roof should satisfy the following requirements:
a. Strength
and Stability: The roof structure should be strong and
stable enough to take up the anticipated loads safely.
b. Weather
Resistance: The roof covering should have adequate
resistance to resist the effects of weather elements.
c. Heat
Insulation: The roof should provide adequate insulation
against heat.
d. Sound
Insulation: The roof should have adequate insulation
against sound from external sources.
e. Fire
Resistance: The roof should offer an adequate degree of
fire resistance in order to give protection against the spread of fire from any
adjacent buildings and to prevent early collapse of the roof. The form of
construction should also be such that the spread of fire from its source to
other parts of the building by way of the roof cannot occur.
f. Day
Lighting: The roof provides daylight in buildings with large floor
area.
Steps and stairs
A step usually consists of
a tread and riser supported by strings. A stair is a structure consisting of a
number of steps leading from one floor to another. The location of stairs in all
types of residential and public buildings should be such as to afford the easiest
and quickest service possible to the building. The main function of the stairs
is firstly to provide a means of communication between the various floors.
Secondly, it also acts as an escape from the upper floors in the event of fire.
Steps
and stairs should satisfy the following requirements:
a. Strength
and Stability: The stairs should be designed like floors
such that they are strong and stable enough to carry the anticipated loads
safely due to the weight of the people using them and also the weight of the furniture
or equipment being carried up or down through them.
b. Fire
Resistance: The stairs should be made of fire-resisting
material and should be connected to different floors, such that they provide
safe means of escape in the event of fire.
c. Sound
Insulation: The stairs should have adequate insulation
against sound from external sources.
d. Weather
Resistance: The stairs if exposed to open air should
offer sufficient resistance to weather elements such as rain and heat.
e. Comfort:
The proper design of steps and proper location of stairs in a building offer
several advantages such as comfort and efficiency in vertical movement, natural
light and ventilation and safety in an emergency.
Finishes for walls
Finishes of several types such as pointing, plastering,
painting and distempering and decorative colour washing are applied on the
walls. The main functions of these finishes are as follows:
a. They
protect the structure, particularly the exposed surfaces, from the effects of
weather.
b. They
provide a true, even and smooth finished surface and also improve the aesthetic
appearance of the structure as a whole.
c. They
cover up the unsound and porous materials used in the construction.
If you find
This information helpful, please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article.








No comments:
Post a Comment