ANTI-TERMITE TREATMENTS IN BUILDINGS
The termite proofing
treatment should invariably be given in all types of buildings during the
construction stage. It is because of the fact that during the post-construction
period, it is extremely difficult and costly to control termite growth. Care
should be taken to ensure that no bridge is formed between any part of the
building and untreated soil. In order to reclaim land by utilizing debris or
filling material, great care should be exercised to ensure that the debris is
termite-free. As far as possible a metal strip or suitable joint filler may be
used to make the floor joints free from termite attack. To check termite
movement from the ground the foundations should be either made of concrete or any
other solid material. Also, care should be taken to ensure that the building
site is free from dead wood, old tree stumps, etc. The superstructure should be
treated with suitable preservatives to make it termite-proof. All the wooden
members like door frames, staircases, etc. should be set on flooring. They
should not be through flooring to prevent ground–soil contact.
Termite proofing methods
Generally, the following two methods are adopted:
a. Chemical treatment of soil
b. Physical structural barriers
Chemical treatment
In order to provide for an effective control of termites,
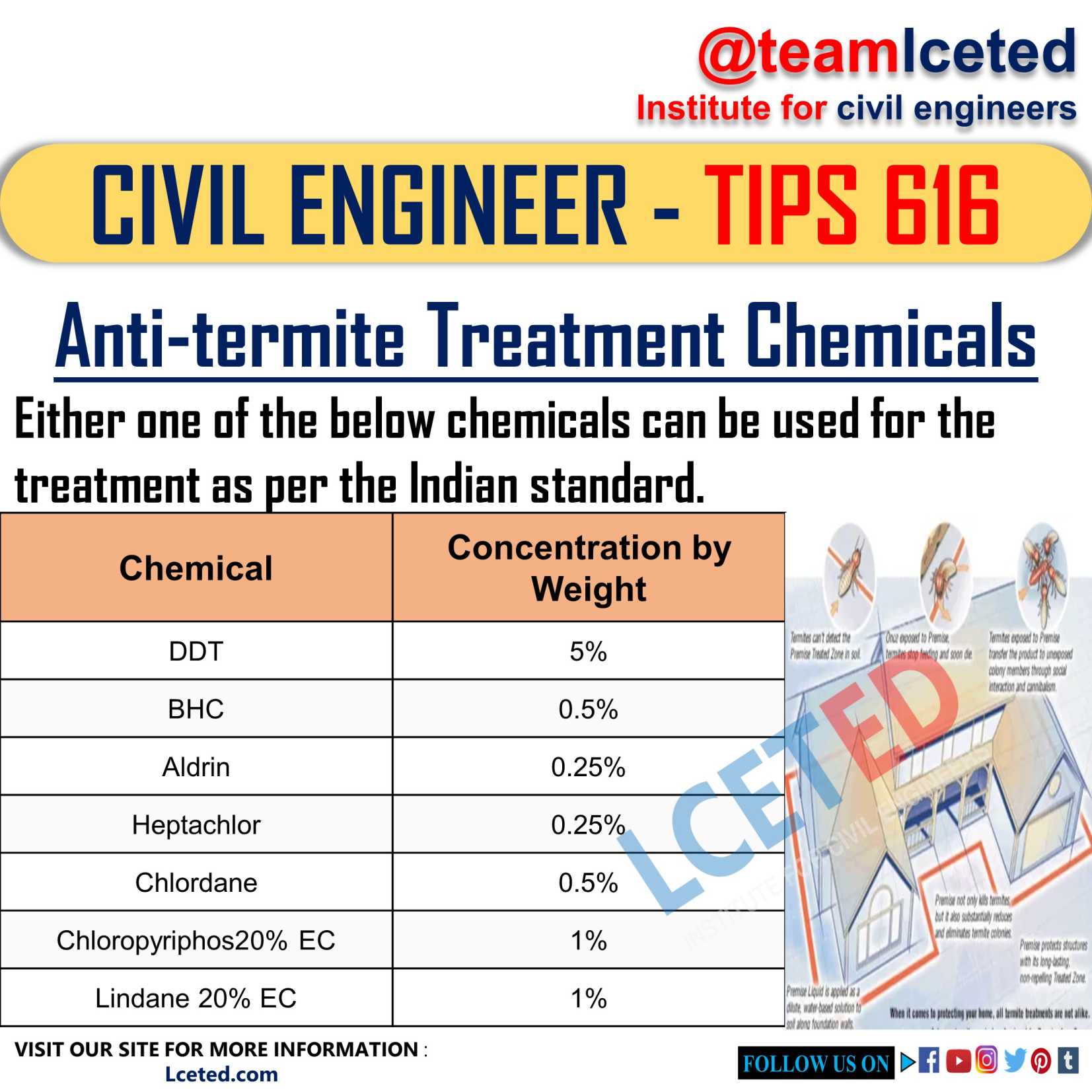
the soil insecticides are thoroughly mixed and evenly spread in the soil. Several
patented insecticides like DDT, BHC and PCP have been generally used. However,
chemicals like Aldrin 0.5 per cent, chlordane 1.0 per cent, Dieldrin 0.5 per
cent and Heptachlor
0.5 per cent by weight in oil solutions or as an
emulsion in water are found to be more successful. All these chemicals are
chlorinated hydrocarbons and are insoluble in water. These chemicals are not
leached away by water and these have proved to be quite effective as a chemical
barrier between the building and ground. These are used in damaged portions of
masonry and woodwork by injecting them under pressure in drilled holes.
Physical structural barriers
Continuous physical structural barriers in the form of a concrete layer or metal layer may be provided at the plinth level. These cement concrete layers should be 50–75 mm in thickness and should preferably be kept projecting about 50–75 mm internally and externally. Metal barriers comprising of non-corrodible metal sheets of copper or galvanized iron having a thickness of 0.80 mm when provided have in certain cases got damaged. Thus, these barriers have not proved to be very effective.
The above post-construction treatments are not low cost and simple. Hence, they should be used only where skill is availableMust read: How
To Do Anti-Termite Treatment For Your Home Foundation?
If you find
This information is helpful, please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article.








No comments:
Post a Comment