In this article, you will be able to know about Shoring
and its components, Factors that determine the design and method of shoring, Procedures
for window/door shore and a vertical shore. Positions and functions of the
members of a shoring team.
WHAT IS SHORING?
Temporary
support for a damaged, collapsed, or partially collapsed structure is unstable,
requiring victims and rescue crews to carry out low-risk search and rescue
operations.
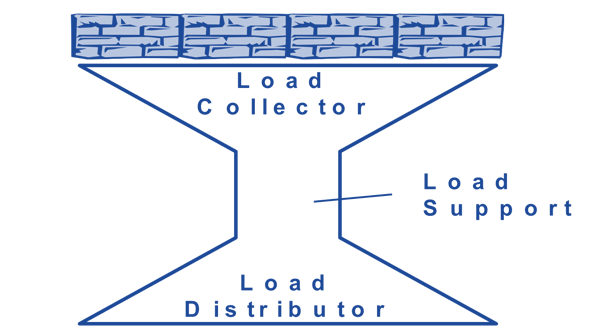
Shoring
follows a “Double-Funnel
Principle”, means that a shore collects a load, channels it and
redistributes it safely to another surface or structure that can support it.
COMPONENTS OF SHORE
Soleplate: Provides a
foundation for the shoring system by supporting the weight being transferred from
above and distributes it over a wider area.
Header beam: collects the weight
from above and spreads it throughout the shoring system.
Post:
Supports
the weight collected by the header and transfers it to the sole plate where it
is distributed.
Diagonal bracing: Locks the entire shoring system together as
one unit, supporting against possible eccentric loads. It is the last component
to be installed.
Gusset
plate: A small piece of 13 mm or 18 mm plywood nailed to the top and bottom of
posts to aid in placement of the header and secure the posts to the header and
soleplate.
Wedges/shims: Two wooden inclined
planes married together and placed under the bottom of the posts. These provide
compression for the shoring system. The shim is a single wedge used to fill in
gaps above the shoring system.
Cleat: A 5cmx10cm wooden piece
nailed to the post and header or sole plate to secure the shoring.
or
A small piece of wood used to secure other
parts of a shoring system.
TYPES OF SHORING
· Vertical
Shoring
· Window/Door
Shoring
Other Types of Shoring
· T-Spot
Shoring
· Raker
Shoring
· Laced
Post Shoring
· Horizontal
Shoring
· Trench
shores
· Pneumatic
shores
·
Improvised Bamboo shoring
DETERMINING FACTOR TO CHOOSE SHORING TYPE
A
variety of factors will determine what method of shoring is required in a
particular situation.
·
Weight of
construction materials
·
Weight of
the structural elements to be supported
·
The normal
load capacity of the existing undamaged structure
·
Condition
of the structure to be supported
·
Condition
of the foundation and floor/surface angle to determine the stability of shoring
·
Availability
of shoring material
·
Lateral and
vertical instability
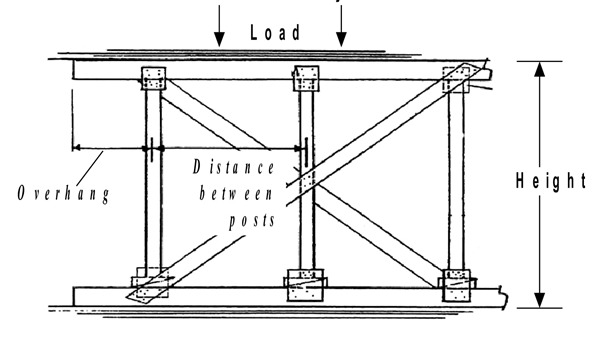
VERTICAL
SHORE SPECIFICATIONS
WITH
10 X 10 cm POST, HEADER AND SOLE PLATE
|
Maximum
Height |
Maximum
Distance Between Posts |
Maximum |
Maximum
Height |
|
2.5 m ( 8’ 0”) |
1.25 ( 4’0”) |
60 cm ( 2’0”) |
3,600 kg ( 8,000 lbs.) |
|
3.0 m ( 10’0”) |
1.50 ( 5’0”) |
80 cm ( 2’6”) |
2,270 kg ( 5,000 lbs.) |
|
3.7 m ( 12’0”) |
1.80 ( 6’0”) |
90 cm ( 3’0”) |
1,600 kg ( 3,500 lbs.) |
Density (weight) of
common building materials
Concrete = 2403 kg/m3
Masonry = 2002.5 kg/m3
Wood = 560.7 kg/m3
Steel = 7849.8 kg/m3
Concrete / Masonry
Rubble = 478.8 Pa
STEPS OF VERTICAL SHORE
1. Determine
where to erect the vertical shore.
2. Measure
and cut sole plate and header.
3. Measure
and cut the posts to the proper height.
4. Attach
cleats or gusset plates to the header and posts, on opposite ends and opposing
sides.
5. Install
the posts and the header on top of the soleplate to support the damaged
structural element
6. Install
a set of wedges under the bottom of each post
7. Attach
cleats or gusset plates on opposite ends and opposing sides of the soleplate
and posts and nail in place
8.
Attach the diagonal braces to each side of
the vertical shore
STEPS FOR WINDOW AND DOOR SHORE
• Locate
where to erect the window/Door shore.
• Measure
the soleplate to cut
• Measure
the header to cut
• Measure
and cut the posts to the proper height
• Install
the soleplate with a set of wedges
• Install
the header with a set of wedges
• Install
the posts and wedges
• Attach
the cleats and/or gusset plate
• Confine
the wedges
• Install
diagonal braces(when applicable)
OTHER TYPES OF SHORING
Several
additional types of shores can be used in collapsed structures, though they
will not be taught in this course. Some examples include:
T-Spot Shore: The
main purpose of the T-shore is to initially stabilise damaged floors, ceilings
or roofs, so that the more substantial shoring can be constructed at less risk.
This shore is quickly placed and only temporary, also used during quick extrication
of a victim.
Raker Shore: A
triangular system of shoring used to support leaning or unstable walls or
columns. Rakers must always be installed in series; at least two must be
erected in any given situation.
Laced Post Shore: A
high-capacity, four-post system that is used to support sagging(Hanging down)
floors and ceilings, or other overhead hazards. It can be used as a “SAFE HEAVEN”.
Horizontal Shore: Used
to stabilise a damaged wall against another undamaged wall in hallways,
corridors or between buildings.
Members and Functions of Shoring team
If sufficient manpower is
available, two separate SIX-person groups can be used to organize a shoring
group, with one team as an assembly team and the other as a cutting board.
However, a team may be
required to perform both sets of duties.
ASSEMBLY GROUP
Shoring
Officer (Rescue Squad Officer): Is responsible for the
process. Works with structural experts (if available) to determine where to
place the shore. If a security guard cannot be assigned, the shore officer will
also accept the role.
Measurer: Measures
all shoring components and publishes information to the layout person of the
cutting board.
Two
Shorers: These work together assembling and erecting shores in
place.
Safety: Responsible
for the overall security of the assembly committee.
Runner: Ensures
that tools, equipment and shoring materials are moved from the primary access
point to the shoring site and help set up shores as needed.
CUTTING GROUP
Cutting
Group Officer (Rescue Squad Officer): Responsible for selecting
the cutting site. The site should be close to the showing function. The cutting
board officer doubles as the safely.
Layout:
Sets up the cutting station and records measurements. Performs all measuring
and layout of angles.
Feeder: The
measured and marked shoring material from the layout to the cutter helps to
protect it while moving and feeding and cutting.
Runner:
follow the requirements related to shoring from shoring station to shoring
site.
Cutter: Measured
materials to be cutted.
Tools
and equipment person: Responsible for monitoring the directions
in which materials and equipment are to be placed and moving, and all
equipment. This person has been appointed to both the cutting committee and the
assembly committee.
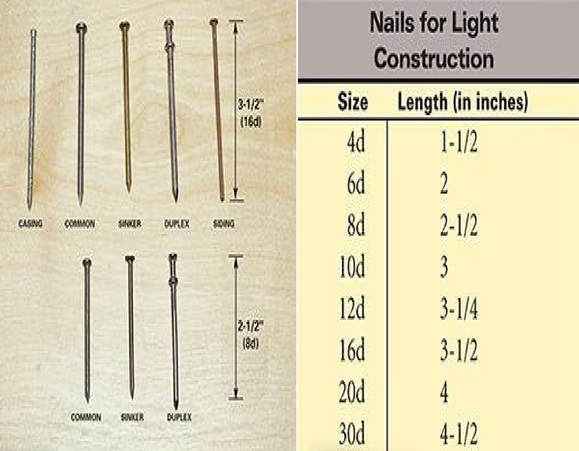
NAIL SPECIFICATIONS
Common nails of two sizes
will be used For CSSR,
All plywood (Gusset plates)
should be nailed using 8D common nails only.
All dimensional wood (100mmx100mmx1800mm)
should be nailed using 16d
Example: For 8d nail
D= diameter of nail (?),
l= length (7.5cm)
x= size of nail (8)
D = l/x • D= 7.5cm/8 = 9.3mm
If you find
This information
helpful, please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article.



















No comments:
Post a Comment