GUIDELINES FOR COLUMNS DESIGN | REQUIREMENTS
FOR COLUMNS DESIGN
Width
of the column, B ≥ 300 𝑚𝑚
and 𝐵/𝐷 ≥ 0.4
Width
of the beam, B ≥ 200 𝑚𝑚
and 𝐵/𝐷 ≥ 0.3
If the span of beam > 5 𝑚 (B ≥ 300 𝑚𝑚 and 𝐵/𝐷 ≥ 0.3)
Better to apply clear
cover of 40 mm to ties NOT to main bars.
Common
bar sizes = 16, 20 and 25 mm.
For preliminary
sizing of columns, use 1% of 𝐴𝑔.
(generally, 1.5-2% in GF, and 1-1.5% in roof)
Practically, max.
area of steel = 3% to avoid congestion at splicing section.
C/C
spacing of main bars ≯
300 mm. In any case, parallel leg spacing of a tie < 300 𝑚𝑚.
No. of bars in 230, 300, 450, 600, 750 sides are 2, 3,
4, 6, 7 #
For proper detailing of the column as well as EQ requirement, min. size of column =
300 mm.
For beams, min. requirement of width is 230 mm so that
at joints beam bars easily pass through column reinforcement.
Min.
4 bars in columns
if the size is 400 x 400 as in that case spacing between
bars is less than 300 mm 400 − 40 × 2 − 8 × 2 − 12 = 292 𝑚𝑚 .
It is advisable to provide additional ties at splicing
location of longitudinal bars.
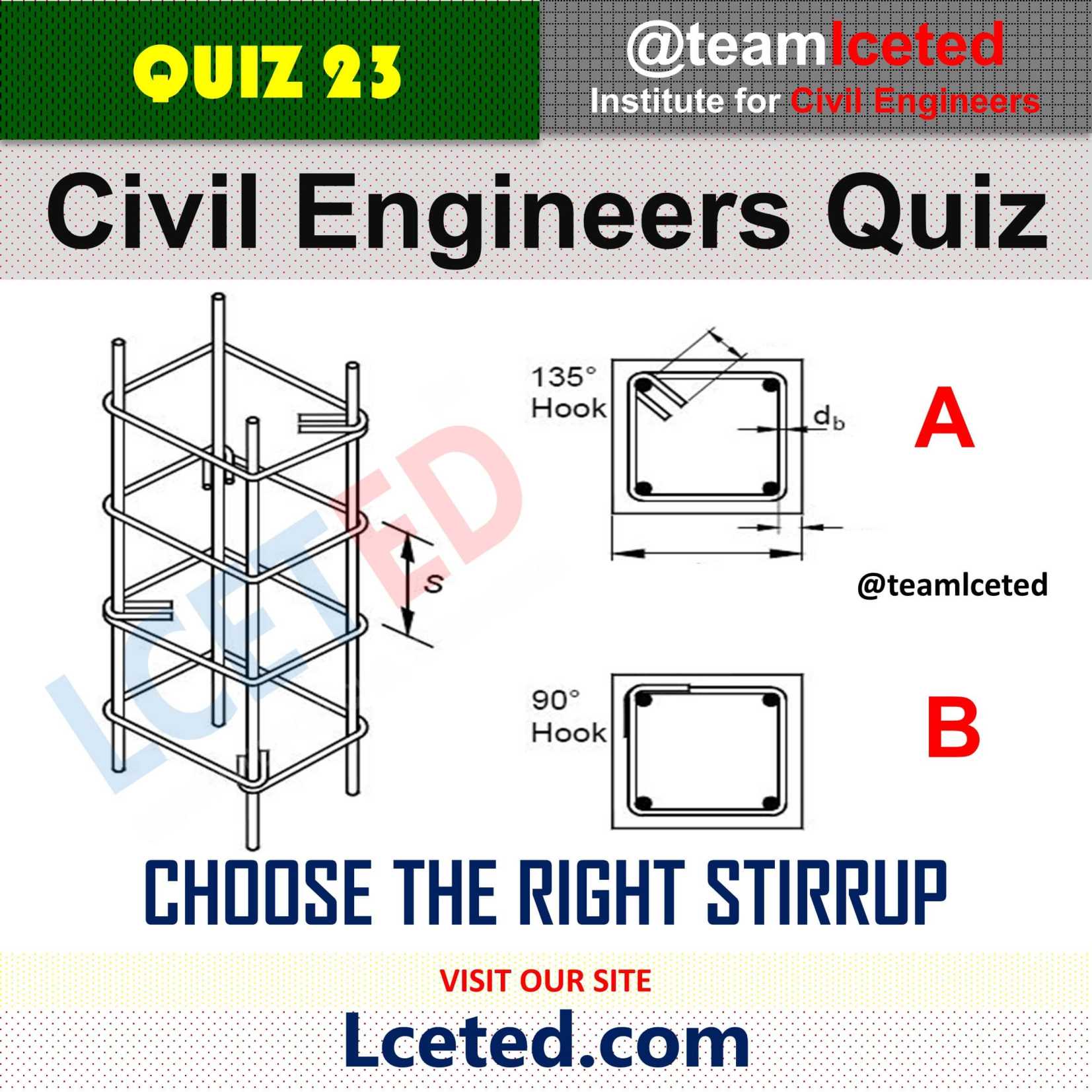
If tie bar is bent through 135˚, then bent length is 8𝜙
For EQ design,
pitch of tie = 1/2 × 𝐿. 𝐿.𝐷.
Maximum distance B/W end restraint ≯ 60 × 𝐿. 𝐿.𝐷 (Columns for aesthetic
purposes near the entrance of buildings).
For EQ design,
lap splices should be only in the central portion of columns beams (away from
plastic hinge locations). Spacing of ties in splice portion = 150 mm.
For EQ design,
lesser spacing of ties near beam/column joint (150 mm)and more spacing towards
centre.
For EQ design,
min. number of bars in rectangular column = 8, for gravity load = 4
For EQ design,
𝜙 𝑡𝑖𝑒 =
8𝑚𝑚.
If 𝜙 𝑙𝑜𝑛𝑔
> 25 𝑚𝑚,𝜙 𝑡𝑖𝑒 =
10𝑚𝑚
For EQ zones,
spacing of longitudinal bars =200 mm or 1/3 the dimension in the considered direction
for (rectangular column) or 1/3 the diameter (circular col.)
It is advantageous to use higher conc. Grade in column
(M 25). Results in less size and steel.
L-,
T, or + shaped columns are often used at outside and
re-entrant building corners for architectural purposes, but they should not be used
in EQ zones as they may crack at re-entrant corners.
Better to provide equal reinforcement on all sides
whether the column is uni-axial or
bi-axial
Above the top of the footing, a pedestal of height 250 mm is
provided with 1#12 𝑚𝑚 𝜙 𝑈 −shaped bars are
provided at each face of the pedestal.
In the design of
column, assume 𝐿𝑒𝑓𝑓 = 𝐿 (this is on safer
side)
Must
read: Plain
Footing Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete | Area Of Shuttering | Area Of
Bitumen Paint
Must
read: Raft
footing Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete | Area Of Shuttering | Area Of
Bitumen Paint
Must
read: Step
footing Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete | Area Of Shuttering | Area Of
Bitumen Paint
If you find
This information helpful, please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article.












No comments:
Post a Comment