What Is Levelling?
The technique of determining the relative altitude of a point on the earth's surface below the earth's surface is called LEVELLING.
Principle Of Levelling
The principle of levelling
is to obtain a horizontal line of sight at which the vertical distance of a point
above or below this line of sight is found.
The Purpose Of Levelling
The
main purpose of balancing in the survey is:
· Find
the heights of the given points in relation to the given data.
· Establishing
points at given heights or at different heights in relation to given or
considered data.
TERMS USED IN LEVELLING
1.
DATUM: Data plane refers to the arbitrary position of a level
surface or other line or surface that calculates any size.
2. REDUCED
LEVEL (RL): The
height or depth of a point above or below the considered data is called the
reduced level.
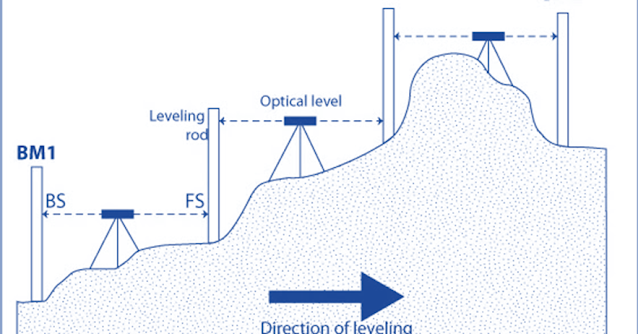
3. BENCH MARK (BM):- B.M. Is the fixed reference point of known height. It can be of the following types.
a. GTS Benchmark (Geodetic
Triangulation Survey): This benchmark is set by state agencies such
as the Survey of India. They are set to the highest precision. The location and
altitude above the MSL are listed in a special catalogue called GTS Maps (100
km apart).
b. Permanent Benchmark: This is a fixed
reference point set by referring to the GTS benchmark (10km intervals).
c. Arbitrary Benchmark: This is the
reference point where the altitude is assumed to be random. For most
engineering projects, the elevation difference is more significant than the
reduced level with respect to the MSL provided in a special catalogue known as
GTS Maps (100 Km. Interval).
4. Mean
Sea Level (M.S.L.): Mean sea level is
an average level of the surface of one or more of Earth's bodies of water from
which heights such as elevation may be measured.
5. Line
of Collimation: Line joining the intersection of the cross-hairs to the optical
centre of the objective and its continuation. It is also known as Line of sight. Line of sight: is defined as the intersection of
the crosshairs and the optical centre of the objective lens.
6. Height
of Instrument (HI): The height of the line of sight with
the considered data is called the HI. - The elevation of the line of. The sight of the telescope. Starting point.
7. Back
sight : (B.S.): The first sight taken on a levelling
staff held at a point of known elevation. B.S. enables the surveyor to obtain HI
+sight i.e. Height of Instrument or line of sight.
8. Fore
Sight (F.S.): It is the last staff reading taken
from a setting of the level. It is also termed as minus sight. Foresight is
the sight taken on a levelling staff held at a point of unknown elevation to
ascertain the amount by which the point is above or below the line of sight.
This is also called minus sight as the foresight reading is always subtracted
from the height of the Instrument.
9. Change
Point (C.P.): The point at which both foresight and rear
view are taken during the levelling process is called the change or shift point.
10.Intermediate Sight (IS): The
foresight taken on a levelling staff held at a point between two turning
points, to determine the elevation of that point, is known as intermediate sight.
Note: one setting of a level, there will be only one backsight
and one foresight but there can be any number of intermediate sights.
If you find
This information helpful please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article.








No comments:
Post a Comment