What Are Setbacks In Construction?
Setbacks
can be defined as the minimum open space around any building or structure.
Municipal regulations state that a certain distance must be maintained between
a building and the boundary of the plot on which the building is to be
constructed. This distance is necessary to ensure that the system is away from
roads, waterways or other buildings. Setbacks are required on the front, back
and sides of buildings and the specifications vary from one area to another.
Each state government has building
policies that are regulated by local government agencies.
There
should not be a permanent system in place for Setbacks that encourage movement
and access. Some elements such as corridors, sunshades and parking area are
allowed to some extent.
IMPORTANCE OF
SETBACKS IN RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS
·
The foundations of
the buildings are built deep underground, which is not visible after
construction. If there are no setbacks, a building can be built anywhere in the
plot and cause inconvenience by infiltrating into another plot. The same is
true for disasters, where if a building collapses, it will not damage
neighbouring property. Recesses should not infringe on the light, privacy and
ventilation of another building.
·
During hazardous
accidents, such as fires, setbacks provide space to access rescue operations
throughout the home. It also helps evacuate residents quickly.
·
If a building is
built in the corner of the plot, it can cause problems with the addition of elements
such as doors and windows. This can cause a lack of ventilation and sunlight in
some areas.
·
Street lanes help
maintain the character of the area and ensure the privacy of residents.
Violation of public property causes problems in parking and more.
· This presents a
unique opportunity for the architect to zoning the plot with landscaping and
other attributes. Better visual access, social design and unique aesthetic
features can be planned.
· Setbacks force
sustainable development patterns in an area and create square scenarios to
create a harmoniously structured environment.
· Setbacks are also
used to provide connection lines for applications such as sewer pipes. There
are some exceptions to side setbacks in row houses, but the building must be
accessed from the front and rear.
SHORT NOTE: What is the importance of a setback?
·
Building Ensuring
that all buildings receive adequate natural light
·
Enough to ensure
adequate ventilation
·
Building
Construction and protection of establishments such as water bodies located near
a building from being adversely affected by human habitation
·
Building To protect
a building from another building shade, it will adequately block ventilation
and sunlight
·
Industries
Protecting buildings from noise-causing elements such as nearby businesses,
airports or highways
·
To ensure easy
access to buildings
The Setback Byelaws Will Primarily
Depend On The Following Factors:
1.
Plot size
2.
It is a one-side or
multi-side open plot
3.
Location or
neighbourhood where the plot is located
4.
The width of the
road where the plot is located
5.
Maximum allowable
coverage area in the area
How Are Setbacks
Calculated?
Some
of the parameters that affect the size of the edge are the type of building,
the height of the building, the size of the plot, the width of the entrance
road, the number of streets in the plot and the zone/location of the plot.
The front lanes (one facing the plot/street / road entrance) have the highest
margin.
Typography
- This refers to the future use of the building.
It can be
·
Residential
·
Commercial
·
Corporate
·
Sports and leisure
·
Industrial
·
Mixed typography
Under them are added several subdivisions.
Size Of The Plot: Setback area required is proportional to the size of
the site. For example, resorts have a large site area to be planned for, so
there is a high setback area. Resorts have a large area, so the size of the
edge is also high.
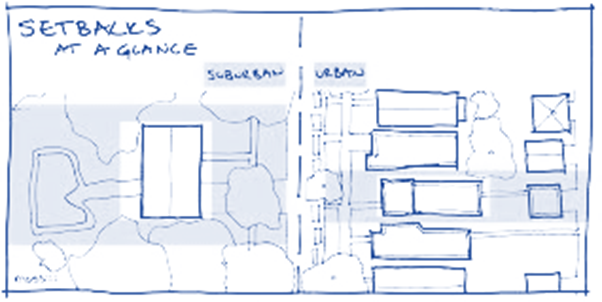
Zone:
This refers to the construction area in the city. Coastal cities have different
development regulations near the coast. River-front developments reveal a
similar phenomenon. There are no setbacks for urban cores; Therefore, there is
active residential and commercial development. The suburbs have very loose
margin rules, favoring lawns and backyards.
The land use map of a city has specially marked zones and falls within their jurisdiction. Some examples are
· 1. Residential Zone
·
2. Industrial Zone
· 3. Commercial Zone
·
4. Institutional Zone
Height
Of The Building: This is the maximum vertical height
measured from the layer level to the highest point of the structure. So the
number of floors in a building is important. This brings up a ratio called FAR
(floor area ratio), which is obtained from the total floor area of the
building to the plot area. The maximum FAR is already specified in the Building
By-Law Code with the maximum floor protection percentage.
Road
width: The width of the road that crosses the plot boundary
proportionally affects the maximum height of the building and the roadside
edge.









No comments:
Post a Comment