CURING OF CONCRETE
WHAT IS CURING?
Curing is
the name was given to the procedures used to improve the hydration of cement and
temperature control and the movement of moisture from the concrete. It plays an important role in the strength development
and durability of concrete.
WHY CURING OF CONCRETE IS IMPORTANT?
Curing is done to control
the rate and amount of moisture loss from the concrete to ensure the
uninterrupted hydration of the Portland cement after the concrete has been
placed and finished in its final stage.
"Drying"
concrete does not reach its design strength or meet the specifications. The
longer the Curing treatment, the better the concrete.
REASONS TO CURE CONCRETE
There
are several important reasons why concrete should be cured:
· Increases
Strength Of Concrete
· Increases
The Durability Of Concrete.
· Harder
And More Abrasion Resistant Surfaces
· Improved
Serviceability
· Improved
Microstructure
Increases Strength Of Concrete
Strength
of concrete increases - Concrete increases in strength with moisture and has a
favourable temperature for hydration of cement.
“Cement, Concrete & Aggregates
Australia" (CCAA) conducted an experimental inquiry into the importance of curing
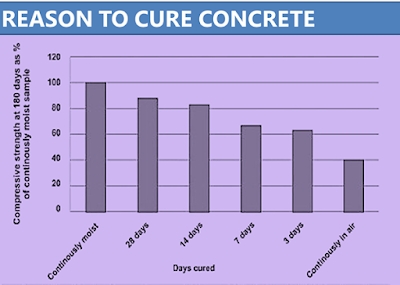
Comparing the strength of
concrete in 180 days of moist curing with various periods of moist curing (0,
3, 7, 14 & 28 days) and then allowing it to dry is illustrated in below
picture.
From the diagram below, it
can be seen that the concrete is allowed to dry immediately, reaching only 40%
of the water strength of the same concrete cured for the entire period of 180
days.
Increases The Durability Of Concrete
The life of concrete is
affected by many factors including its permeability, porosity and absorption.
Well-cured concrete reduces
heat, plastic and drying shrinkage cracks, making concrete more watertight,
thus preventing moisture and water-dispersing chemicals from entering the
concrete, thus increasing its durability.
Improved Serviceability
Concrete that is allowed to
dry quickly undergoes considerable shrinkage at an early age. Improper curing
contributes to weak, dusty surfaces having poor abrasion resistance.
Improved Microstructure
Material
properties are directly related to their microstructure. The curing cement
hydration reaction progresses smoothly and forms a calcium silicate hydrate
gel, which binds the aggregates leading to a rock-solid mass, reducing the porosity of the concrete and improving the physical and mechanical properties
of the concrete.
DURATION OF CURING
The curing time of concrete
depends on the Grade and type of cement, the mixing ratio, the desired concrete
strength, the shape and size of the concrete member and the environmental and
exposure conditions. The duration can vary from a few days to a month.
In the case of ordinary Portland cement (OPC), the
exposed concrete surfaces shall be kept continuously wet or wet conditions by
by covering them with sacks hessian
cloth or other similar material or ponding,
and shall be kept continuously moist for at least 7 days at as of the date of
pouring.
Therefore, concrete used with mineral admixtures or
mixed cement, it is recommended to extend the above minimum periods to 10-14
days to facilitate the secondary reaction.
Curing Requires Adequate Moisture, Temperature & Time
If
any of these factors are neglected the desired properties will not develop.
METHODS TO CURE CONCRETE
Methods
of curing concrete are widely included in the following categories:
Water Curing: the
loss of moisture from the concrete surface prevented by constantly wetting the exposed surface of the concrete.
Membrane Curing: Reducing
Moisture Loss from Concrete Surface by covering it with an impermeable
membrane.
Steam Curing: Raising
the temperature of concrete and by keeping surface wet will accelerate
accelerate the rate of strength gain
1. WATER CURING
Ponding: This is the most common and
cost-efficient method of curing flat surfaces such as concrete slab, flat
roofs, pavements, and other horizontal surfaces.
A dike around the edge of
the slab, which may be sub-divided into
smaller dikes is erected and filled with water to create a shallow pond. Care
must be taken to ensure that the pond water does not dry out as it can lead to
an alternate drying and wetting condition.
Wet Coverings: Water-absorbent
cloth such as hessian, burlap, cotton mats, rugs, etc. can be used to cover the
entire surface and maintain water on the concrete surface as soon as the
concrete is set. Due to the capillary action, they must be constantly moist to
prevent water from absorbing from the concrete body.
Sprinkling, fogging & mist curing: The use of a good spray or
mist or water mist is an efficient method of water supplying to the concrete
surface especially during hot weather, which helps to reduce the temperature of
the concrete and ultimately retains moisture inside the concrete body.
2.
IMPERMEABLE MEMBRANE CURING
This process done Occasionally,
concrete work is carried out in areas with severe water shortages.
The amount of water
normally mixed to make concrete is more than enough to hydrate the cement, and
this water is not allowed to leave the concrete body.
The concrete is covered by
a membrane, which effectively clogs the vapour from the concrete.
Formwork Leaving
the formwork at an early age of the concrete is one of the most effective
methods of healing, especially for columns. However, turning the time of the
formwork is significantly reduced.
Plastic Sheeting: Plastic
sheeting forms an effective barrier to control moisture loss from the concrete
surface, provided they are secured in place and protected from damage. They
should be placed immediately after the final set of the concrete without
causing any damage to the surface.
On flat surfaces such as slabs, pavements, etc., they
must be properly secured to the surface and must extend beyond the edges of the
slab, so that they are not blown away by gusts of wind.
Membrane curing compounds:
The curing compounds are
wax, acrylic and water-based liquids, which are sprayed onto the newly finished
concrete, forming a membrane that reduces the loss of moisture content from the
concrete. These are low-cost methods of healing that are difficult to follow
with standard procedures.
When
used to cure concrete, application time is critical for maximum performance.
They should be used when the free water on the surface evaporates and there is
no water sheen on the surface. Very early application dilutes the membrane,
where too late application is absorbed into the concrete. Care should be taken
to avoid foot, machinery and vehicle traffic on the concrete surface to prevent
damage to the finish.
3.
STEAM CURING
Steam curing is a process
of accelerating the initial hardening of concrete and mortar by exposing them
to steam and moisture.
This type of system is
commonly used for precast concrete products that are manufactured in the
factory and have a very fast turning time of formwork.
In the curing chamber, the
control of temperature and humidity is of prime importance or else the concrete
products are likely of fracture, crumble and develop other problems later in
their service lives.
This
type of curing systems are generally adopted for railway sleepers, concrete
blocks, pipes, manhole covers, poles, pipe culverts, prestressed precast
concrete products, and so forth.
CURING IN HOT WEATHER
1. In
hot weather, concrete should be protected from over-drying and direct sunlight
and wind.
2. Curing
materials that reflect sunlight should be used to reduce the temperature of the
concrete.
3. Wet
curing is recommended and care should be taken to avoid excessive stress.
4. Caused
by alternate wetting and drying or by cold water on hot concrete. canvas
tarpaulins or sun shades framed enclosures can be used to protect concrete from
direct sunlight.
CURING IN COLD WEATHER
1. Some
problems associated with a temperature below 4 ° C are:
2. Freezing
of concrete before adequate strength has developed
3. Slow
development of concrete strength
4. Thermal
stresses induced by cooling hot concrete to colder ambient temperatures.
5. In
cold weather, certain procedures such as heated enclosures, insulating blankets
and curing products may be used.
6. The temperature of fresh concrete should be kept above 100 ° C using heated raw materials and hardening should be continued for a longer period until the concrete acquires the desired strength.
CONCLUSION
1. Chemical
reactions between cement and water form the C-S-H gel, which binds to the
concrete material. Coarse and fine aggregates, mineral compounds etc. turn
these pieces into a rock-solid mass.
2. This
is only possible if the treatment is continuous for at least 14 days;
Regardless of the type of cement used.
3. With
a dense microstructure and flawlessness, prolonged curing can lead to improved
longevity.
4. Well-formed
concrete can give poor life if not properly cured, on the other hand moderately
designed concrete will give better life if well treated. So the importance of curing
should never be ignored.
5. At
many sites, concrete curing is left to the end and comfort of the unskilled
worker.
6. Site
engineers and supervisors should make extra effort to ensure that on-site
healing is not neglected and that they provide the resources needed for a
satisfactory level of healing using the best technique available on site.
7. Just
like a newborn baby, when it comes to this world, it needs great care for its
growth and protection from this new environment, similarly, newly placed
concrete needs proper protection and care from the environment and aggressive
environment.
8. Strict
adherence to good curing practices on site will help the concrete achieve the
properties of designed strength, improved durability, improved microstructure
and longer service life.
If you find
This information helpful please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article.













No comments:
Post a Comment