A
structure is made up of many connecting building elements such as walls, beams,
columns, foundations, slabs. Of these, the slab is the most important. This
allows other parts of the building elements to withstand different loads. There
are different types of slabs in construction. But in this article we have
discussed in detail the types of concrete slabs.
What is a Slab in Construction?
A
slab is a structural element that is made of concrete, which is used to create
flat horizontal surfaces such as floors, roofing floors and roofs. A slab is
usually several inches thick typically between 100 and 500 mm thick and is
supported by beams, columns, walls or floor.
TYPES OF CONCRETE SLAB USED IN
CONSTRUCTION
1. FLAT SLAB
2. CONVENTIONAL SLAB
3. HOLLOW CORE RIBBED SLAB OR HOLLOW CORE SLAB
4. HARDY SLAB
5. WAFFLE SLAB
6. SUNKEN SLAB
9. COMPOSITE SLAB
10. LOW ROOF SLAB
11. PROJECTED SLAB
12. WAIST SLAB
1.
FLAT SLAB
Flat
slab is also known as beam-less slab because it is supported directly by columns or
caps. Here, the loads are transferred directly to the columns.
The function of this type of slab is to provide a plain ceiling surface, which will
give the best diffusion of light. They are commonly used in hotels, parking
lots, commercial buildings or places where beam projections are not suitable
for height controls or even aesthetics view.
ALSO READ: What
Is Flat Slab? | Application Of Flat Slabs | Advantages And Disadvantages Of
Flat Slab
2.
CONVENTIONAL SLAB
A
slab supported by beams and columns is called a conventional slab or regular
slab. In these types, the thickness of the slab is small, while the depth of
the beam is large and it is transferred to the load-bearing beams and then to
the columns. This requires more formwork compared to the flat slab. It is not
necessary to provide column caps on the regular type slab.
ALSO READ: What Is
Conventional Slab | Types | Advantages | Disadvantages
3.
HOLLOW CORE RIBBED SLAB OR HOLLOW CORE SLAB
It
name derived from the cores or voids that run through the units. The cores can
act as service pipes and will undoubtedly reduce the self-weight of the slabs
and increase structural efficiency. Cores also have the advantage of stability
by reducing the amount of material used.
4.
HARDY SLAB
This
type of slab is built with hardy bricks which is made of hollow bricks and
concrete. These bricks are used to fill thick slab areas, which saves the
amount of concrete, thus reducing the slab's weight. These types of slab are
commonly found in Dubai and China. This slab is used in areas where the
temperature is very high. The thickness of the slab is increased to withstand
the temperature from above the slab. The heat coming from the walls is
counteracted by using special bricks that contain thermocoles.
ALSO READ: What
Is Hardy Slab | Types | Application | Advantages | Disadvantages
5.
WAFFLE SLAB
Waffle
slab is a also called grid slabs. It is a reinforced concrete roof or floor with a square grid with deep sides. This type of slab is mainly used for good picture
viewing and installation of artificial lighting at the entrances of hotels, malls and restaurants.
This
is a type of slab where you can see that there is a hallow hole in the slab
when the formwork is removed. PVC sheets (pieces) are first placed on the
shutter, then reinforcement is provided between the pieces and a steel mesh is
provided above the pod, which is then filled with concrete. After the concrete
sets, the formwork is removed and the PVC pieces are not removed. This creates
a hollow hole in which a hole is closed at one end.
This
type slab is mainly used for industrial and commercial buildings, while wood
and metal waffle slabs are used on many construction sites.
ALSO READ: What
Is Waffle Slab? | Types | Advantages And Disadvantages
6.
SUNKEN SLAB
This
type slab used below the washrooms to cover sewer pipes or WC pipes or other
equipment is called a sunken slab. Care should be taken to avoid leakage
problems as the water pipes are hidden below the ground.
Proper
waterproofing and treatment of the slab provided to prevent leakage or
moisture. After sending the sewer pipes in the slab, the slab is filled with
broken bricks or coal or suitable lightweight material.
The
slab that is provided below the normal level of the floor at a depth of 200mm
to 300mm and filled with pieces of broken brick is called a sunken slab.
or
The slab that is provided above the normal floor level at a height of 200mm to 300mm and filled with coal or pieces of broken bricks called the sunken slab.
7. PRESTRESSED CONCRETE SLAB
a)
Pre-Tensioned Slab:
The
steel tensioned in slab before placing the concrete is called the pre-tensioned
slab. The slab has the same features of post-tension.
b)
Post-Tensioned Slab:
The
slab in which the steel cables or tendons are tensioned after concreting is
called the post-tensioned slab. Reinforcement is provided to resist
compression. In this slab, the reinforcement is replaced with steel cables /
tendons.
This type slabs break the natural
weakness of the concrete in tension and makes better use of its strength in
compression.
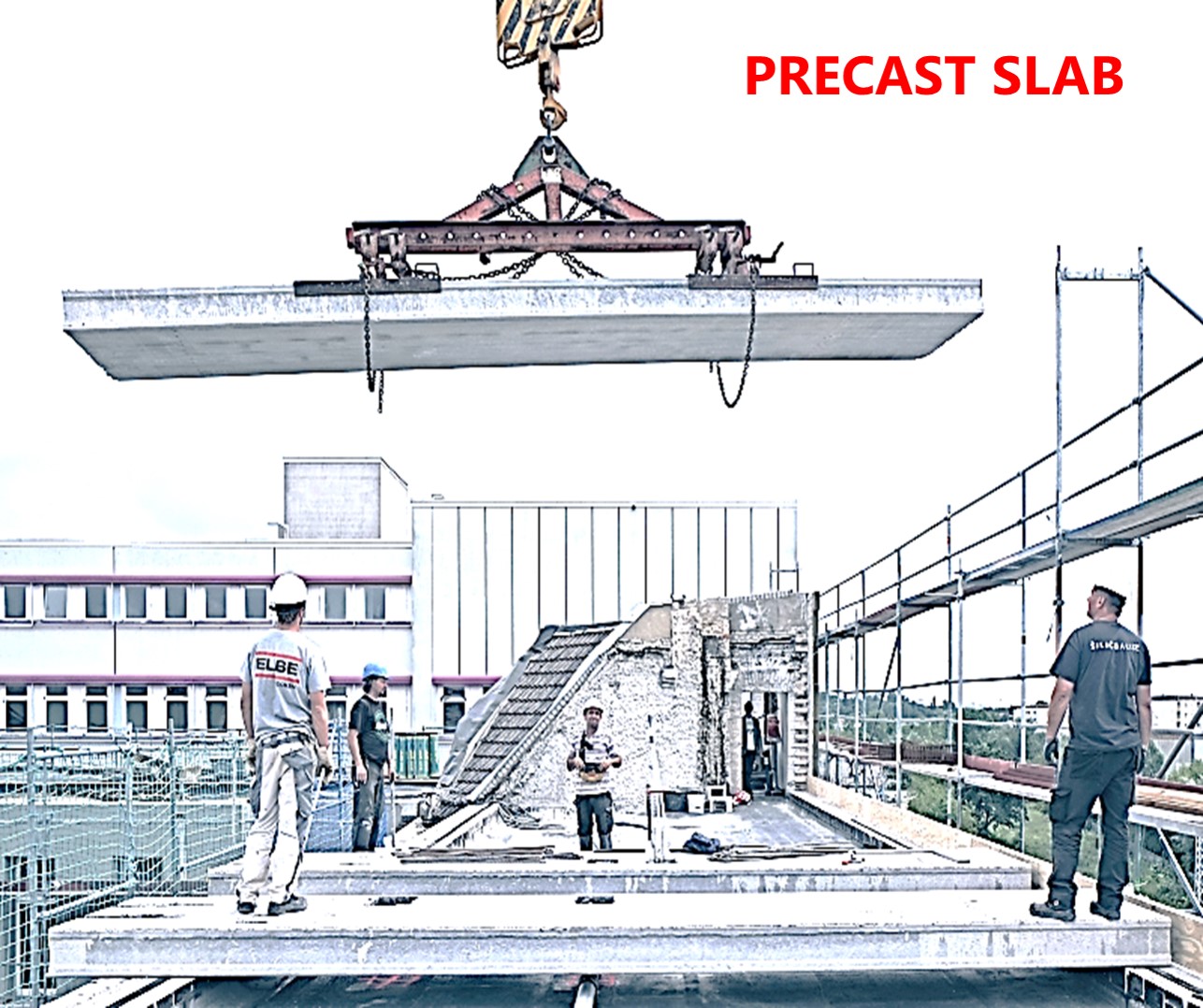
8. PRECAST SLAB
Precast concrete slabs are embedded in fabrication plants and cured, after which they are supplied for erection. The greatest advantage of precast concrete slabs is that they are manufactured in the plant, which increases their performance and achieves high-quality control over concrete slabs on site
Additionally,
precast concrete slabs can be found to be about 24% cheaper than cast-in-place
concrete slabs. Even if you spend more on assembly, you save a lot on formwork.
The
most commonly used precast slab types are channel and double T types.
9.
COMPOSITE SLAB
Typically, it is built on
reinforced concrete castings on top of a profile steel base. During the
construction phase the decking acts as a working area and formwork, and also
acts as an external reinforcement during the life of the slab.
10.
LOW ROOF SLAB
The
slab provided above the door for storage is called a low ceiling (roof) slab.
This type of slab closes at all ends and opens at one end. This slab is just
below the actual slab and above door and window level. This type of concrete
slabs are used in homes.
11.
PROJECTED SLAB
A
slab that is fixed on one side and free on the other is called a projected slab
or cantilever slab. These types of slab are usually built in hotels,
universities, function halls, etc to use that area for picking or dropping up
zone and for unloading and loading area. This is one of the types of concrete
slabs.
12.
WAIST SLAB
The
Waist Slab is
nothing more than a normal slab with some inclination angle between the two
supports. (Mainly used on RCC stairs).
The
Waist Slab rests
from the beam to the beam and the main stair reinforcement steel goes up to the
middle of the resting beam. The thickness of the waist slab depends on the
length of the stair flow. Usually the thickness is 5 ″ or 6 of.
The Waist
Slab
has three types of reinforcements;
·
Main steel
·
Distribution steel
·
Extra top.
Function of Slab
01. It gives a flat surface
02. To support loads
03. It gives heat fire, and
sound insulator
04. The top layer becomes
the roof for storey below it
05. The space between the ceiling
and slab can be used to place building applications
Effective Span of the RCC Slab
The effective span of slab should be lesser of the two
L = Center to centre distance between
the support
L = Clearspan + d (effective depth of
slab)
Minimum Thickness of Concrete Slab
The slab thickness is decided based on length of span to depth ratio as given in IS 456: 2000.
Must
read: What is
Lintel? | Types of Lintel | Uses | lintel length Calculation | lintel bearing
Must
read: Hardy
Slab Calculation | Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete & Area Of
Shuttering
Must
read: Waffle
Slab Calculation | Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete & Area Of
Shuttering
Must
read: Pitch
Roof Calculation | Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete & Area Of
Shuttering
Must
read: Semi‐Round
Stair‐Case Calculation | Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete & Area Of
Shuttering
Must
read: Lift-Pit
Calculation | Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete And Area Of Shuttering
Must
read: Ramp
Calculation | Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete & Area Of Shuttering
Must read: Dome Slab Calculation | Quantity Survey | Volume Of Concrete | Area Of Shuttering

















No comments:
Post a Comment